The modern Linux distributions have out of the box terrific support for most of the available hardware components, like graphics cards, printers and WiFi adapters. But it is always possible that the setup procedure doesn’t come up directly with the correct or most optimized drivers. In this tutorial I will show you how to install graphics drivers in Linux Mint.
- Activate Nvidia Driver Linux
- Install Nvidia Drivers Linux Mint
- Install Proprietary Nvidia Drivers Linux Mint
- Linux Update Nvidia Drivers
- Nvidia Linux Drivers Ubuntu
- Can't Install Nvidia Drivers Linux Mint
- Install Nvidia Drivers Linux Mint 13
Check current driver for graphics cards
The objective of this artcile is to guide reader thought the installation of NVIDIA drivers on Linux Mint. This article will discuss three methods of Nvidia driver installation in the following order: Automatic Install using standard Linux Mint Repository; Manual Install using the Official nvidia.com driver; Operating System and Software Versions. Please Donate to support us to buy new equipment to improve video quality. 🔶 Please subscribe help us to reach 10000 sub.
When you installed Linux Mint and you actually see icons and colors and text on your display you would probably think that the operating system installed the correct driver for your graphics card. And the chances are that the correct driver has indeed been installed, but it is always best to have a look if the that’s is actually the case or maybe some generic driver has been chosen that will not give you the maximum feasible performance. To see what choices the operating system made for your graphics card you can first do the following:
1) Connect your computer via a network cable or via Wifi.
2) Open the applications menu.
3) Choose Driver Manager under the Administration category and enter your password.
First a cache update takes place, so the most recent software list will be gathered.
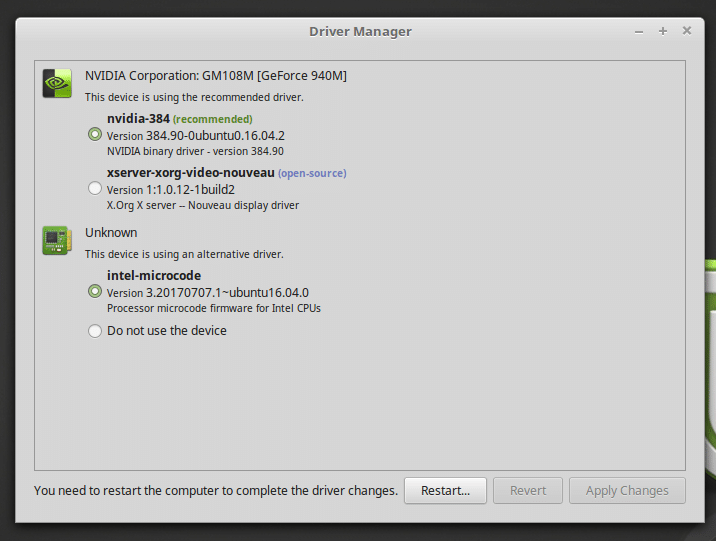
After the standard cache update takes place, Driver Manager displays an overview of device components that require a driver. Now probably both open source and proprietary drivers will be shown for your graphics card.
Install nvidia driver via Driver Manager
As the previous image shows the operating system recognizes a GTX 750 Ti graphics card and gives you the option to install an open source driver or a proprietary nvidia driver.
1) Choose the recommended driver (indicated with highest number and Recommended).
2) Click on Apply changes.
Install latest nvidia driver via PPA
When you have a very new graphics card it is possible that the Driver Manager will not give you the most recent driver. A sign for that is if the Driver Manager only shows an open source option for your graphics card. But also in the before mentioned example of the GFX 750 Ti, which is already a couple of years old, there are newer drivers available. You can check if there is a newer version on the nvidia drivers page.
1) Go to the nvidia driver page.
2) Fill in your product type, product series, product and operating system.
3) Click on search.
Here we see that there is a newer driver (410), as the driver that was available in the previous example was version 390.
The most convenient way to get access to the newer driver is not by installing the driver from the nvidia website, but by using the PPA (Personal Package Archive) “ppa:graphics-drivers”. Although I said in earlier tutorials that I want to stay away as much as possible from the command line, now we actually need it.
To add the PPA do the following:
1) Open a terminal via Ctrl + Alt + T or by search for terminal in the applications menu search bar.
2) type the following command in the terminal and hit enter:
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:graphics-drivers/ppa
3) You will get the message “Press Enter to continue or Ctrl+C to cancel”. Hit enter to continue.
4) When the command has been finished type in the terminal the following command and hit enter:
sudo apt-get update

When the command has been finished you can set the correct driver.
5) Open the applications menu.
6) Choose Driver Manager under the Administration category and enter your password.
Now you will see that there are more driver alternatives available, including the newest nvidia-driver-410.
7) Select the newest driver, in this case 410, and click Apply Changes.
8) When changes have been applied click on Restart…
After your computer has been restarted the newest driver should be active.
Install driver for AMD graphics cards via Driver Manager
If you have an AMD graphics card and you did the steps in the first paragraph “Check current driver for graphics cards” then your graphics card probably has been recognized and gives you the option to install an open source driver or a proprietary AMD driver, indicated with fglrx.
1) Choose the recommended driver (indicated with highest number and Recommended indicator).
2) Click on Apply changes.
Install latest AMD driver via PPA
Although your AMD graphics card will probably work fine out of the box in Linux Mint, there could be different reasons to install a more recent driver. It is possible to install AMD proprietary drivers that can be downloaded from the AMD drivers page, but in Linux it is a bit of a tricky process. Much easier is to add the available PPA to your operating system.
To add the PPA do the following:
1) Open a terminal via Ctrl + Alt + T or by search for terminal in the applications menu search bar.
2) type the following command in the terminal and hit enter:
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:oibaf/graphics-drivers
You will get the message “Press Enter to continue or Ctrl+C to cancel”.
3) Hit enter to continue.
4) When the command has been finished type in the terminal the following command and hit enter:
sudo apt-get update
When the command has been finished you can set the correct driver.
5) Open the applications menu.
6) Choose Driver Manager under the Administration category and enter your password.
Now you will see that there are more driver alternatives available.
Mar 12, 2015 Micheal Swan is the author of book practical english usage. This is the oxford version. Practical english usage is a international student's edition. You can download this book for free here. Practical English Usage.pdf - Free download Ebook, Handbook, Textbook, User Guide PDF files on the internet quickly and easily. Here you can find practical english usage pdf shared files. Download Michael swan practical english usage pdf from mediafire.com (27 MB), Practical English Usage.pdf from mediafire.com 15.34 MB free from TraDownload. Practical English Usage by Michael Swan PDF Download. Michael Swan Practical English Usage 3rd, 4th edition PDF. Download Swan practical English usage for grammar learning. The book is intended for higher level students of English and for teachers. Being a reference book, it contains information at various levels, ranging from relatively simple points to quite. Practical english usage pdf download.
7) Select the newest driver and click Apply Changes.
8) When changes have been applied click on Restart…
After your computer has been restarted the newest graphics driver should be active.
Updating your kernel
Another option to have better driver support is probably not the first thing you’ve thought about, namely upgrading to a newer kernel. If you are already on a recent release of your distribution, you probably already have very up to date drivers, but if you are using for example Linux Mint 17, which was released in May 2014, it is based on an old kernel. When you use an old Linux Mint distribution you can upgrade to the most recent version. If you are already on the most recent version you can still upgrade the kernel, as new kernels are released frequently and often contains driver updates. Upgrading a kernel deserves a completely separate tutorial, so I mention it here for information only.
Final words
Although people have the tendency to always want the newest and greatest, with everything it is advisable to think first about why you actually want to update to the latest drivers or the most recent Linux distribution or the most recent application. If it is not broken don’t fix it, is a frequently recurring saying. If your current distribution recognizes your graphics card out of the box and everything works fine, just be happy. But only if it doesn’t work properly or if you have specific performance related or feature related requirements for your graphics card, of course than you should try to setup the latest drivers. Or as I wrote in the previous paragraph, it maybe is safer to upgrade the Linux kernel, as there are newer graphics driver already available.
Introduction
This is Linux Mint 18, codename Sarah.
Important links
Tips
Moving windows which don't fit in the screen
If your screen resolution is too low, some windows might not fit in the screen.
While pressing the ALT key, you can grab any part of a window with the mouse and move it across the screen.
Installing multimedia codecs offline
To download the multimedia codecs into an installable archive:
- Boot from the Linux Mint ISO on a computer which is connected to the Internet
- Open a terminal and type 'apt download mint-meta-codecs' (without the quotes)
- This creates a 'mint-meta-codecs.tgz' archive
On computers which do not have an Internet access, you can decompress this archive and run ./install.sh (or alternatively 'sudo dpkg -i *.deb') to install the multimedia codecs.
Booting with non-PAE CPUs
To boot Linux Mint 18 on CPU which do not officially support PAE (Pentium M processors for instance), please use the 'Start Linux Mint with PAE forced' option from the boot menu.
Watching Flash DRM content
To watch videos from a video/replay/VOD website using Flash with DRM, please follow this tutorial: http://community.linuxmint.com/tutorial/view/2028
Solving freezes
Some graphics cards don't work well with the open-source driver present in Linux Mint.
If Linux Mint freezes during boot time, use the 'nomodeset' boot option as illustrated in the video below:
Activate Nvidia Driver Linux
After the installation, reboot the computer and hold SHIFT to force the boot menu to appear.
Add the 'nomodeset' option as illustrated below:
Note: If you're using an Optimus card, you've nothing more to do. Upon reboot, a system tray icon should show up indicating which GPU is currently active. Click on it to switch GPUs.
Note: If you still cannot boot try one of the following solutions:
- Try with 'nouveau.noaccel=1' instead of 'nomodeset'.
- Use the 'Compatibility mode' to boot and install Linux Mint.
- After the installation, use 'Advanced Options' -> 'Recovery mode' from the boot menu and choose 'resume'.
Choosing the right version of Linux Mint
Each new version comes with a new kernel and a newer set of drivers. Most of the time, this means newer versions are compatible with a larger variety of hardware components, but sometimes it might also introduce regressions. If you are facing hardware issues with the latest version of Linux Mint and you are unable to solve them, you can always try an earlier release. If that one works better for you, you can stick to it, or you can use it to install Linux Mint and then upgrade to the newer release.
Note that during a 'point upgrade' (for instance between Linux Mint 17.2 and 17.3), the kernel and hardware drivers are not impacted, so you get all the new features without risking regressions on hardware support.
Important information
New backport component in repositories
In previous releases, Linux Mint repositories had 3 components enabled by default: main, upstream and import.
Install Nvidia Drivers Linux Mint
This was changed in Linux Mint 18:
The backport component is now also required and enabled by default.
If you're upgrading manually from a previous release, please make sure to add this component to your APT sources.
AMD Catalyst (fglrx) drivers
The AMD Catalyst (fglrx) drivers are not compatible with Xorg 1.18, which is the version used in Linux Mint 18.
These drivers are proprietary and so their code is not available. AMD indicated they no longer wanted to support them and urged their customers to use open-source drivers instead.
If you are using an ATI GPU in Linux Mint 18, the operating system will either select the Radeon or AMDGPU drivers for you, and these are installed by default.
UEFI support
UEFI is fully supported.
Linux Mint is not certified by Microsoft (and should not need to be). If your computer is using 'secureBoot', turn it off.
Install Proprietary Nvidia Drivers Linux Mint
Note: If you really need secureBoot, you will need to use rEFInd and sign the kernel with a MOK).
Known issues
Sound and microphone issues
If you're facing issues with your microphone or your sound output, please install 'pavucontrol'.
This will add 'PulseAudio Volume Control' to your menu. This application has more configuration options than the default volume control.
Linux Update Nvidia Drivers
LSB dependency issue with Epson drivers and Google Earth
A missing package prevents the installation of the Epson drivers and of Google Earth.
This is a known issue upstream in Ubuntu which should soon be addressed. You can follow the progress on this issue in this bug report.
Mouse cursor disappears with Intel GPU
The mouse cursor disappears after switching users or suspending the computer. This is a known issue. Click here to see the upstream bug report.
Nvidia Linux Drivers Ubuntu
Freezes/Crashes with ASRock Skylake motherboards
A known issue is affecting ASRock Skylake motherboards. The kernel floods /var/log/syslog with messages until the disk runs out of space.
If you are suffering from this issue add 'echo 'disable' > /sys/firmware/acpi/interrupts/gpe6F' into your /etc/rc.local (to edit this file with admin privileges, you can type 'gksu xed /etc/rc.local').
For more information on this issue, please visit https://forums.linuxmint.com/viewtopic.php?f=49&t=223180.
DVD Playback with VLC
If VLC does not find your DVD player, click on Media->Open Disc, and specify '/dev/sr0' as the disc device.
Issues with KDE apps
If you're experiencing issues with KDE apps (Okular, Gwenview, KStars.etc) run the following command:
- apt install kdelibs-bin kdelibs5-data kdelibs5-plugins
Force UEFI dialog hanging the installation
The following bug is affecting Linux Mint: https://askubuntu.com/questions/693732/window-stuck-on-force-uefi-installation-window.
The issue occurs in EFI mode, when the HDD (or SSD) is new (without a partition table) and the installer is connected to the Internet.
To work around this problem, disable your Internet connection before launching the installer, or let the installer partition your drive automatically first (during a first install) and then install a second time with manual partitioning.
For more information on this bug, visit https://bugs.launchpad.net/ubuntu/+source/ubiquity/+bug/1418706.
Can't Install Nvidia Drivers Linux Mint
Other issues
Install Nvidia Drivers Linux Mint 13
Linux Mint 18 is based on Ubuntu 16.04. Make sure to read the Ubuntu release notes.